Our recent work advances data-driven and optimization-based methodologies for the design and analysis of high-performance engineering systems, with a focus on accelerating design workflows while improving functional accuracy and robustness.
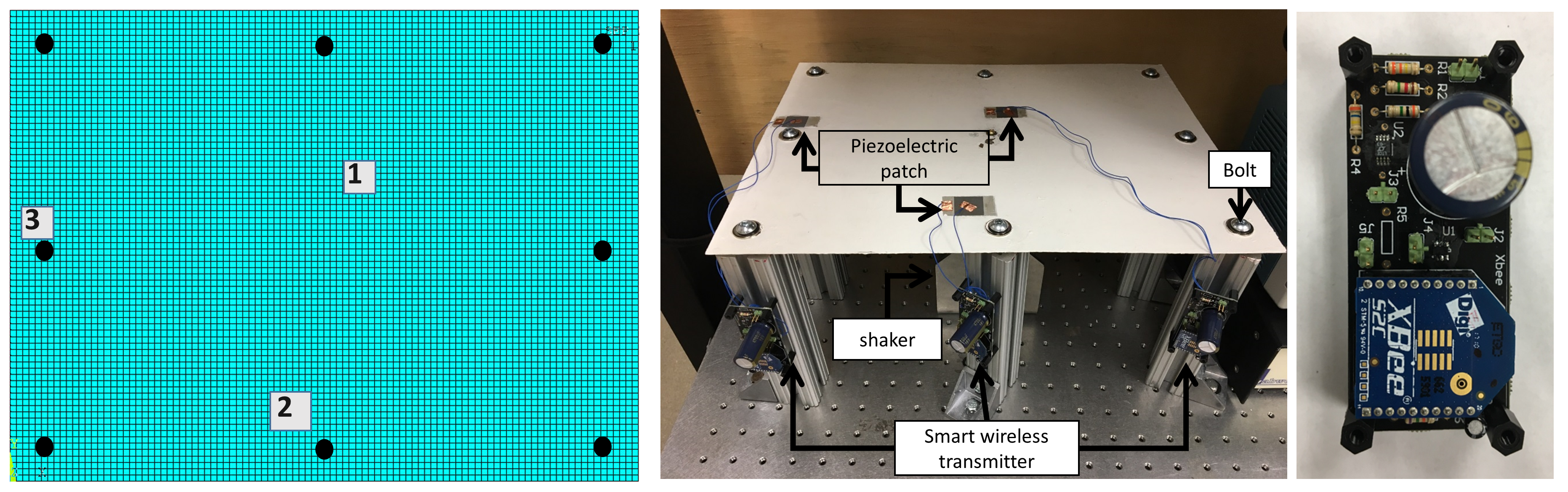
Sensor network design under uncertainty: Multifunctional structural materials possess attractive attributes that can be designed to realize smart system functionalities such as integrated sensing systems for failure diagnostics and prognostics. With the integrated sensing capabilities, real-time monitoring of potentially damaging structural responses becomes possible. However, due to various uncertainties introduced by structural material properties, manufacturing processes, as well as operating conditions, ensuring the robustness of sensing performance is of vital importance for smart sensing system development. This research presents a data-driven robust design approach to develop piezoelectric materials based structural sensing systems for failure diagnostics and prognostics. In the proposed approach, a detectability measure is defined to evaluate the performance of any given sensing system, and the sensoring system design problem can be formulated to maximize the detectability for different failure modes by optimally allocating piezoelectric materials into a target structure. This formulation can be conveniently solved using reliability-based design framework to ensure design robustness while considering the uncertainties.
 |
|
| Piezoelectric sensor design for joint monitoring (left); Experimental verification (middle); Smart wireless transmitter for battery free monitoring (right) |
Related recent papers:
 |
Neural Network-Based Surrogate Model in Postprocessing of Topology Optimized StructuresNeural Computing and Applications, 2025 This paper presents a neural network–based surrogate modeling framework for |
 |
Custom Multi-Component Force Transducer Design Using Topology OptimizationEngineering Research Express, 2025 This study presents a topology optimization–based design methodology for |
 |
Reinforcement Learning–Based Delay Line Design for Crosstalk MinimizationIEEE Access, 2024 This paper introduces a reinforcement learning–based framework for the |